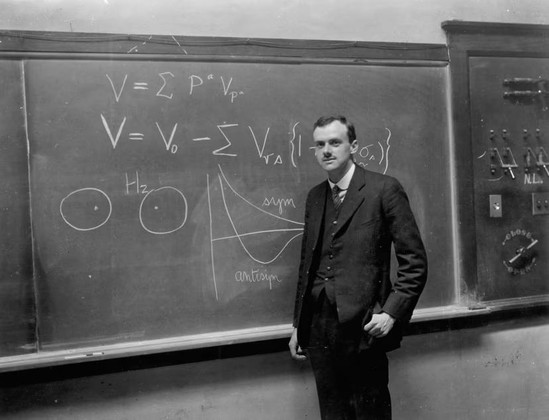Recent searches
Search options
#quantummechanics
#OTD in 1914.
The Franck–Hertz experiment, the first electrical measurement to clearly demonstrate the quantum nature of atoms, was presented to the German Physical Society.
Their experimental results proved to be consistent with the Bohr model for atoms that had been proposed the previous year by Niels Bohr.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Franck%E2%80%93Hertz_experiment
Niels Bohr at PG:
https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/author/44167
https://www.europesays.com/uk/45735/ QSA Research Highlights Molecules as Elements in Quantum Computing #AllJournalNews #Computing #DOEScienceNewsSource #LawrenceBerkeleyNationalLaboratory #Nature(journal) #Newswise #QuantumComputing;QuantumComputers;quantumTechnology;QuantumInformationScienceAndTechnology #QuantumMechanics #Technology #UK #UnitedKingdom
Abrikosov vortices (fluxons) are quantum of magnetic flux (Φ~hc/e) which appear in type-II superconductors (SC) induced by persistent current loops. Fluxons allow magnetic fields to penetrate a type-II SC causing magnetic pinning. #Science #Physics #QuantumMechanics See: doi.org/10.1038/srep...
`Unlike any other clock, this quantum watch does not utilize a counter and is fully quantum mechanical in its nature. The quantum watch has the potential to become an invaluable tool in pump-probe spectroscopy due to its simplicity, assurance of accuracy, and ability to provide an absolute timestamp, i.e., there is no need to find time zero.`
https://journals.aps.org/prresearch/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevResearch.4.043041
2/3…there is very often a group of people talented enough to be grappling with core technical principles but more comfortable as “spokespersons” due to not having physics or other degrees.
Well, we can and should help these people. Many of them understand at a basic level for instance -the issue of the incommensurate status between #QuantumMechanics and #Relativity. We have these typically known equivalences between matter and energy…but then the notion of #Information that requires neither…
https://www.europesays.com/uk/34322/ This Is My Top Quantum Computing Stock for 2025, and It’s Not IonQ or Rigetti Computing #CloudComputing #Computing #MarketEstimates #MarketOpportunity #Microsoft #QuantumComputing #QuantumMechanics #RigettiComputing #Technology #UK #UnitedKingdom
Negative Time in Quantum Physics: A UToronto Study Challenges Our Understanding
Scientists at the University of Toronto have observed negative time values in quantum experiments! This mind-bending discovery challenges our understanding of time in the quantum realm, suggesting time can seemingly move backward. Fascinating! #QuantumPhysics #NegativeTime #TimeTravel #QuantumMechanics #ScienceNews #UniversityofToronto
https://tech-champion.com/general/negative-time-in-quantum-physics-a-utoront...
Is #GenderTheory too complicated for its own good? It's time we #KillOurDarlings, question our theories, and move forward, just like #TheoreticalPhysics must do to escape #QuantumMechanics.

Researchers discover a new type of quantum entanglement
https://phys.org/news/2025-04-quantum-entanglement.html #quantum #quantumphysics #physics #science #quantummechanics #astrophysics

https://www.europesays.com/uk/29742/ What exactly would a full-scale quantum computer be useful for? #Computing #QuantumComputing #QuantumMechanics #Technology #UK #UnitedKingdom
Many-worlds without necessarily many worlds?
IAI has a brief interview of David Deutsch on his advocacy for the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics. (Warning: possible paywall.) Deutsch has a history of showing little patience with other interpretations, and this interview is no different. A lot of the discussion centers around his advocacy for scientific realism, the idea that science is actually telling us about the world, rather than just providing instrumental prediction frameworks.
Quick reminder. The central mystery of quantum mechanics is that quantum systems seem to evolve as waves, superpositions of many states, with the different states interfering with each other, all tracked by a mathematical model called the wave function. But when measured, these systems behave as localized particles, with the model only able to provide probabilities on the measurement result. Although the measurement results as a population show the interference patterns from the wave function. This is often called the “wave function collapse”.
Various interpretations attempt to make sense of this situation. Many deny the reality of what the wave function models. Others accept it, but posit the wave function collapse as a real objective event. Some posit both a wave and particle existing throughout. The Everett approach rejects wave function collapse and argues that if we just keep following the mathematical model, we get decoherence and eventually the same observations. But that implies that quantum physics apply at all scales, meaning that it’s not just particles in superpositions of many states, but measuring equipment, labs, people, planets, and the entire universe.
Reading Deutsch’s interview, it occurred to me that my own structural realist outlook, a more cautious take on scientific realism, is reflected in the more cautious acceptance I have of Everettian quantum mechanics. People like Deutsch are pretty confident that there is a quantum multiverse. I can see the reasoning steps that get them there, and I follow them, to a point. But my own view is that the other worlds remains a possibility, but far from a certainty.
I think this is because we can break apart the Everettian proposition into three questions.
- Does the mathematical structure of quantum theory provide everything necessary to fit the current data?
- If so, can we be confident that there won’t be new data in the future that drives theorists to make revisions or add additional variables?
- What effect would any additions or changes have on the broader predictions of the current bare theory?
My answer to 1 is yes, with a moderately high credence, maybe around 80%. I know people like Deutsch and Sean Carroll have this much higher. (I think Carroll says his is around 95% somewhere on his podcast.) And I think they have defendable reasons for it. Experimentalists have been stress testing bare quantum theory for decades, with no sign of a physical wave function collapse, or additional (hidden) variables. Quantum computing seems to have taken it to a new level.
But there remain doubts, notably about how to explain probabilities. I personally don’t see this as that big an issue. The probabilities reflect the proportion of outcomes in the wave function. But I acknowledge that lot of physicists do. I’m not a physicist, and very aware of the limitations of my very basic understanding of the math, so it’s entirely possible I’m missing something, which is why I’m only at 80%.
(Often when I make the point about the mathematical structures, it’s noted that there are multiple mathematical formalisms: wave mechanics, matrices, path integrals, etc. But while these are distinct mental frameworks, they reportedly always reconcile. These theories are equivalent, not just empirically, but mathematically. They always provide the same answer. If they didn’t, we’d see experimental physicists trying to test where they diverge. We don’t because there aren’t any divergences.)
If our answer to 1 is yes, it’s tempting to jump from that to the broader implications, the quantum multiverse. (Or one universe with a much larger ontology. Some people find that a less objectionable description.)
But then there are questions 2 and 3. I have to say no to 2. The history of science seems to show that any claims that we’ve found the final theory of anything is a dubious proposition, a point Deutsch acknowledges in the interview. All scientific theories are provisional. And we don’t know what we don’t know. And there are the gaps we do know about, such as how to bring gravity into the quantum paradigm. It seems rational to wonder what kind of revisions they may eventually require.
Of course 3 is difficult to answer until we get there. I do doubt any new discoveries would drive things toward the other interpretations people currently talk about, or overall be less bonkers than the current predictions. Again given the history of science, it seems more likely it would replace the other worlds with something even stranger and more disconcerting.
So as things stand, there’s no current evidence for adding anything to the structure of raw quantum theory. That does imply other worlds, but the worlds remain untestable for the foreseeable future.
To be clear, I don’t buy that they’re forever untestable. We can’t rule out that some clever experimentalist in the future won’t find a way to detect interference between decohered branches, to recohere them (which has been done but only very early in the process), or some other way we haven’t imagined yet.
My take is the untestability of the other worlds means that Everettian quantum mechanics, in the sense of pure wave mechanics, shouldn’t be accepted because we like the worlds, or rejected because we dislike them. For now, the worlds should be irrelevant for a scientific assessment. The only question is whether anything needs to be added to the bare theory, a question, it should be noted, we can ask regardless of whether we’re being realist or antirealist about any of this.
All of which means that while my credence in austere quantum mechanics is 80%, the credence for the other worlds vacillates somewhere around 50%. In other words I’m agnostic. This resonates with the views I’ve seen from a number of physicists, such as Stephen Hawking, Sidney Coleman, John Preskill, and most recently, Brian Cox, which accept the Everett view but downplay the other worlds. Even Sean Carroll notes in one of his AMAs that he doesn’t really care so much about the other worlds, but the physics at the core of the theory.
But maybe I’m missing something. Are the questions I raised above as easy to separate as I’m thinking? Or are there problems with pure wave mechanics I’m overlooking?
The End is Near for___________ (fill in with today’s panic button).
#Physics
#Democracy
#Asparagus
…about the physics. What’s left are hard problems. We’ve picked off all the low hanging fruit. The #StandardModel still wins #Survivor in terms of fitting (most) observations, experimental or otherwise. #Protons have not suddenly started decaying. #QuantumMechanics still helps us find ways to beat alleged limits on circuit building in spite of #Relativity getting the kids on the weekend
January 1928: The Dirac equation unifies quantum mechanics and special relativity
A seminal paper by Paul Dirac, who relied on mathematical intuition, laid the foundation for quantum electrodynamics.
By Nyla Husain (from the archives)
https://www.aps.org/apsnews/2024/11/mathematical-intuition-dirac-quantum-mechanics
What Is Hidden In The Core Of A Neutron Star?
a jumble of Feynman diagrams and coloured shapes with a Bauhaus feel.
#linocut #printmaking #physics #Bauhaus #quantumMechanics #FeynmanDiagram #penguinDiagram #particlePhysics #sciart #WorldQuantumDay
*I am somewhat dubious of this date because a) I was trained to use the metric convention day/month/year and b) physicists use the reduced constant h-bar (that’s h divided by 2 pi) and then, cause it’s easier they just change units such that h-bar = 1 but it’s as good an excuse as any
3/3



![Gustav Hertz
The American Institute of Physics credits the photo [1] to AB Lagrelius & Westphal, which is the Swedish printmaker used by the Nobel Foundation for most prints/engraving of its book series Les Prix Nobel. - http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1925/hertz-bio.html Gustav Hertz
The American Institute of Physics credits the photo [1] to AB Lagrelius & Westphal, which is the Swedish printmaker used by the Nobel Foundation for most prints/engraving of its book series Les Prix Nobel. - http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1925/hertz-bio.html](https://files.sfba.social/cache/media_attachments/files/114/392/357/494/072/505/small/16420631071be9c3.jpg)